THE LEGEND
OF STANDOFF 13
OF STANDOFF 13



The Standoff cyberbattle has its very own backstory, one that immerses participants in the context and spirit of the upcoming confrontation. Previously, the legend was only revealed at the event itself, but this year we decided to make it public knowledge.
Below you can learn about the history of the two states, their key indicators, and development trends. Sharp-eyed attackers might even find hints for triggering critical events.
Below you can learn about the history of the two states, their key indicators, and development trends. Sharp-eyed attackers might even find hints for triggering critical events.
What you will find in this document
The Legend of Standoff 13
Since 2016 the international virtual arena has been home to State F, which is steadily expanding its influence. As the state has developed, more and more hackers have been eyeing its companies' systems with a view to penetrating them in any way possible.
In 2024, a new player emerged on the cyberscene—the young and technologically advanced State S. Although the state was formed only recently, its rapid economic growth has piqued the interest of neighboring nations, and its unprecedented rate of technological development has attracted hackers. As a result, hackers now have an expanded array of targets, while defenders face a substantial increase in their protective duties.
Despite the competition between the two nations, businesses follow market economy trends and seek to reduce production costs, so a number of companies operate in both countries at once.
What will come of all this, we’ll see at Standoff 13.
In 2024, a new player emerged on the cyberscene—the young and technologically advanced State S. Although the state was formed only recently, its rapid economic growth has piqued the interest of neighboring nations, and its unprecedented rate of technological development has attracted hackers. As a result, hackers now have an expanded array of targets, while defenders face a substantial increase in their protective duties.
Despite the competition between the two nations, businesses follow market economy trends and seek to reduce production costs, so a number of companies operate in both countries at once.
What will come of all this, we’ll see at Standoff 13.
State F


Geography
State F is a continental nation with a long coastline. Its primary waterway, the Off River, springs from the Magnetic Mountains in the south of the country, and almost immediately turns into a wide lowland river.
State F is rich in natural resources: vast deposits of oil, iron ore, uranium ore, coal, and natural gas.
State F is rich in natural resources: vast deposits of oil, iron ore, uranium ore, coal, and natural gas.
Demographics
Since 2019, the population has been increasing by approximately 15 percent annually.
Most citizens of State F reside in the capital city. The vast majority of adults have completed higher or postgraduate vocational education. Interest in the IT industry—and information security in particular—is snowballing, so more and more citizens are gaining skills in these areas.
Most citizens of State F reside in the capital city. The vast majority of adults have completed higher or postgraduate vocational education. Interest in the IT industry—and information security in particular—is snowballing, so more and more citizens are gaining skills in these areas.
Economy and industries
The primary drivers of State F’s economy are logistics, IT, human services, nuclear, and oil.
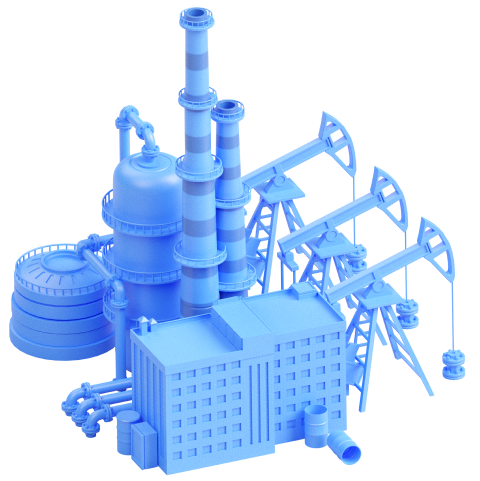
Oil and gas
Key organization: Tube
Key organization: Tube
Thanks to its vast oil and gas reserves and the accelerated development of generating capacity over the past 20 years, State F has become the world’s leading exporter of natural resources. The key market player is Tube, which has long been developing the oil industry in State F; as of this year, the company has expanded its geography of operations State S.
Within State F, Tube owns oil production facilities. A drilling platform has been installed at an offshore oilfield. The crude is extracted using pumpjacks, also known as nodding donkeys, then exported for refining.
The company also owns a gas distribution plant that supplies gas to industries and the public.
Within State F, Tube owns oil production facilities. A drilling platform has been installed at an offshore oilfield. The crude is extracted using pumpjacks, also known as nodding donkeys, then exported for refining.
The company also owns a gas distribution plant that supplies gas to industries and the public.
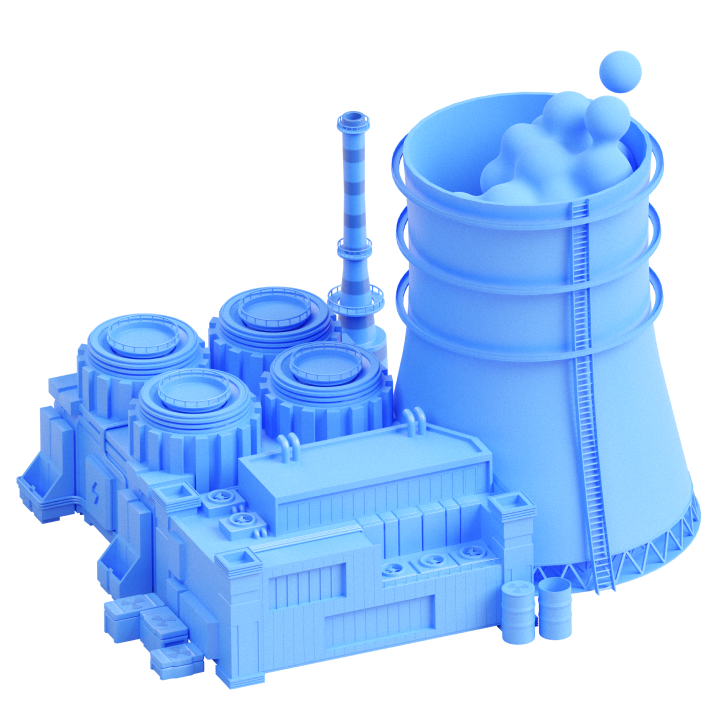
Nuclear industry
Key organization: Atomic Energy
Key organization: Atomic Energy
State F recently resumed development of uranium reserves for civilian purposes, constructing an ore enrichment plant and the first nuclear power plant (NPP). Previous hacker attacks had frozen the sector’s development, but the government allocated funding to revitalize operations. Atomic Energy is responsible for the construction and operation of these facilities. The purpose of developing the industry is to diversify energy sources amidst the ongoing energy crisis.
Unlike thermal power plants (TPPs), NPPs cause virtually no air pollution, and power generation itself is cheaper. The country’s government is keen to stress its "atoms for peace" philosophy. State F currently has one NPP in operation, providing 6 percent of total electricity production, with plans to develop the industry further. To this end, Atomic Energy has established a closed nuclear fuel cycle.
Unlike thermal power plants (TPPs), NPPs cause virtually no air pollution, and power generation itself is cheaper. The country’s government is keen to stress its "atoms for peace" philosophy. State F currently has one NPP in operation, providing 6 percent of total electricity production, with plans to develop the industry further. To this end, Atomic Energy has established a closed nuclear fuel cycle.
Uranium ore mining
Uranium enrichment
Fuel production
NPP energy production
Disposal of spent material




The NPP has a high level of system automation:
— Industrial control systems (ICS) manage the operating modes of turbines and generators;
— Microprocessor-based relay protection terminals are installed at the NPP’s electrical substation.
At the uranium enrichment plant, the centrifuges are operated using a Siemens controller, which regulate the speed of rotation in cascades through a Vacon frequency converter. A similar system was used at the Iranian facility targeted by the Stuxnet attack.
— Industrial control systems (ICS) manage the operating modes of turbines and generators;
— Microprocessor-based relay protection terminals are installed at the NPP’s electrical substation.
At the uranium enrichment plant, the centrifuges are operated using a Siemens controller, which regulate the speed of rotation in cascades through a Vacon frequency converter. A similar system was used at the Iranian facility targeted by the Stuxnet attack.
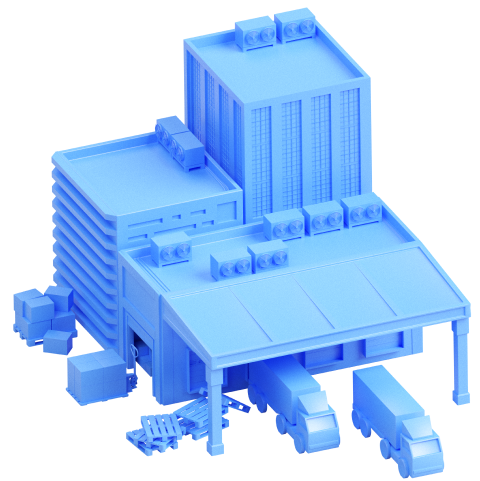
Transport and logistics
Key organization: Heavy Logistics
Key organization: Heavy Logistics
In State F, Heavy Logistics holds a monopoly over the main infrastructure facilities for transportation of goods and passengers.
Airport
Rail facilities
Heavy Logistics is continually modernizing the airport to improve customer comfort. For example, thanks to the automation of the baggage claim process and use of a greater number of boarding bridges, the duration of passenger boarding and disembarking procedures has decreased by a factor of three.
Rail facilities include the railway with trains, switches, and level crossings.
The railway in State F is used to convey both passengers and cargo, including oil and petroleum products, as well as fuel for the thermal power plants.
The railway in State F is used to convey both passengers and cargo, including oil and petroleum products, as well as fuel for the thermal power plants.
Sea cargo and river passenger ports
Most goods are exported and imported through the cargo port. It has warehouses and a parking lot for trucks. A railway line leads to the seaport. The port has a container crane for quick loading and unloading of container ships, plus an overhead crane for moving containers from the warehouse to the railway track.
For residents and visitors, the company operates a tourist riverboat route along the Off River.
For residents and visitors, the company operates a tourist riverboat route along the Off River.
Traffic light systems in the capital
FastShip courier service
The company diligently monitors the condition of traffic lights to ensure maximum safety for drivers and pedestrians.
The courier service is responsible for the timely and reliable delivery of goods to consumers.





The company also operates the amusement park’s cable car and parking lot, the park itself being owned by City Housing and Utilities.

Utilities and public services
Key organization: City Housing and Utitilies
Key organization: City Housing and Utitilies
City Housing and Utilities was one of the first organizations established in the country. With the emergence of State S, the company shifted its focus there and transferred most of its services there. However, the company continues to maintain a presence in State F, where it owns two key facilities.

Water intake and treatment facilities
The facilities are essential for providing the general public with high-quality drinking water, regulating chlorine levels, and treating wastewater.

Amusement park
The amusement park is a high-tech complex with cultural and entertainment areas and attractions, the centerpiece of which is the Ferris wheel with next-gen management system.

Information technology
Key organization: STFware
Key organization: STFware
Despite a digitalization drive, only this year did the country get its own IT company, STFware. The company is responsible for operating the servers of the Nodenest hosting provider and developing commercial software. These include its flagship product, Open City, that provides a platform for interaction between citizens and government agencies, and a ticket sales service.
The company boasts a young, progressive management that takes the security of its employees and users very seriously.
The company boasts a young, progressive management that takes the security of its employees and users very seriously.

Space
Sadly, in 2024, State F was forced to suspend its space program due to a rise in hacker attacks on the CosmoLink Labs infrastructure. Funding was reallocated to industries deemed more critical for citizens. The country may resume development in this area in the future.
State S


Geography
State S shares a border with State F. The northeastern part of the locality, which makes up 15 percent of the country’s area, is known for its arid climate.
In the southern part of State S lies a large lake, one of the biggest on the continent. The country produces ores, combustible natural resources, rare earth metals (a large deposit of which was recently discovered), and industrial minerals (graphite, gypsum, sulfur).
In the southern part of State S lies a large lake, one of the biggest on the continent. The country produces ores, combustible natural resources, rare earth metals (a large deposit of which was recently discovered), and industrial minerals (graphite, gypsum, sulfur).
Demographics
Although the population of State S is still comparatively small, migration ensures a steady increase. Over 40 percent of the country’s people, natives and migrants, reside in the capital. Young people make up a significant portion of the population, leading to a high percentage of online service users within the country.
Economy and industries
State S is actively developing its oil and gas, metallurgy, power, and finance industries, rolling out services to improve quality of life.
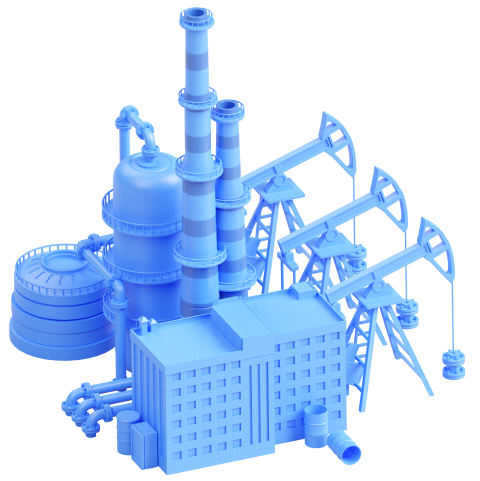
Oil and gas
Key organization: Tube
Key organization: Tube
The oil and gas industry, considered one of the most promising in the country, is wholly managed by Tube. Tube’s operations began in State F, but with the emergence of State S, the company transferred part of its production there.
Within State S, Tube carries out the following processes.
Within State S, Tube carries out the following processes.
Pumping
From the pumping station, the oil is transported through the pipeline to the tank farm and refinery.
The oil pipeline is the only connection link between the oil extraction and refining sites
Storage
Refining
The tank farm, or oil depot, consists of special systems for storing oil and petroleum products, situated in an enclosed area.
Each tank is equipped with fire extinguishing and liquid level control systems to prevent overflow.
Each tank is equipped with fire extinguishing and liquid level control systems to prevent overflow.
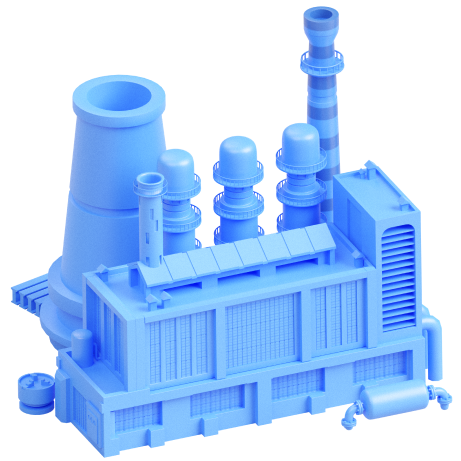
The oil refinery is a complex industrial facility that includes oil cargo piers, electric dehydrators, tube furnaces, fractionating columns, a hydrocracking unit, control panels, and other equipment.
At the oil refinery, oil first passes through an electric dehydrator for the removal of salt and water. It then goes to a tube furnace where it is heated up to a certain temperature. After that, the heated oil is separated into fractions in a fractionating column.
Finished petroleum products are delivered to the storage facilities. At the hydrocracking unit, residual oil refining products are used to produce gasoline, jet fuel, and diesel fuel.
At the oil refinery, oil first passes through an electric dehydrator for the removal of salt and water. It then goes to a tube furnace where it is heated up to a certain temperature. After that, the heated oil is separated into fractions in a fractionating column.
Finished petroleum products are delivered to the storage facilities. At the hydrocracking unit, residual oil refining products are used to produce gasoline, jet fuel, and diesel fuel.
Transportation
The refined oil is exported by rail. An automated on-spot station is used to load oil into rail tankers quickly, safely, and without leaks.







Tube is constantly on the lookout for new areas of development, so, besides oil and gas enterprises, the company owns paint-and-varnish, tire, and bitumen plants.
Metallurgy
Key organization: MetalliKO steel mill
Key organization: MetalliKO steel mill
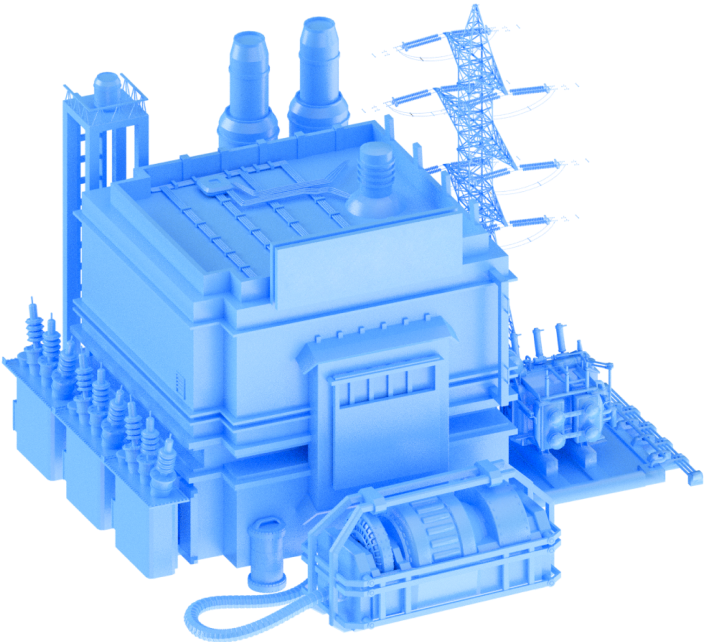
The metallurgical industry is fully controlled by MetalliKO, a company striving to embrace automation and technological advancements. Despite a certain conservativeness in the industry, the plant’s top management continuously works on improving business processes and developing the company, and so more and more IT solutions are being introduced at MetalliKO.
The metallurgy industry in State S is divided into two areas.
The metallurgy industry in State S is divided into two areas.

Ferrous metallurgy
Mining and beneficiation of ferrous metal ores, production of cast iron and steel, rolling of ferrous metals.

Non-ferrous metallurgy
Mining and beneficiation of non-ferrous metal ores, production of non-ferrous metals and their alloys.
The management of MetalliKO took the decision to open a workshop for processing rare earth ores.
Energy sector
Key organizations: TPP, HPP, WPP, SPP
Key organizations: TPP, HPP, WPP, SPP
The power industry of State S consists of electricity generation, transmission, and distribution facilities.

TPP
State S has built a number of TPPs, which account for approximately 70 percent of the generating capacity. These plants also supply heating to the public.

HPP
In line with global trends for eco-friendly technologies and use of renewables, a hydroelectric power plant (HPP) was constructed on the Off River; it supplies almost 20 percent of energy production.

WPP
The proximity of the sea made it possible to tame the wind and build several wind farms, or wind power plants (WPPs). Wind farms contribute a combined 3 percent of total energy, but this share is expected to increase soon due to the global energy crisis.

SPP
Also operating in the country are solar power plants (SPP). This accords with the concept of distributed energy generation.


Substation No. 1

Substation No. 2
All energy generated at the power plants is distributed to two substations, which then transmit electricity through power lines.


Power transmission lines (PTL)


Cities, towns, and villages

Factories and enterprises

Transport and telecommunication systems

Export
The sales company supplies electricity to the population and keeps records of energy consumption. Smart meters have been installed nationwide, allowing the company to:
— Remotely control the load and cut off persistent non-payers;
— Digitalize electricity metering.
The state’s energy system is managed from the dispatch control center.
— Remotely control the load and cut off persistent non-payers;
— Digitalize electricity metering.
The state’s energy system is managed from the dispatch control center.

Utilities and public services
Key organization: City Housing and Utilities
Key organization: City Housing and Utilities
City Housing and Utilities was founded in State F, but as it grew, it expanded its presence into State S as well. The company owns a range of infrastructure assets of perennial interest to hackers. Here are the key ones.

Safe City urban video surveillance system»
Safe City urban video surveillance system was created to combat crime. Information from cameras is fed to the Unified State IT Platform.

IoT devices in homes
New homes in State S are being equipped with ever more IoT devices. For example, they can control and automatically adjust the lighting and heating.

Parking lot
Entrances to the parking lot near the mall are equipped with automatic barriers with license plate recognition. The system calculates the time a vehicle spends in the parking lot and issues a payment ticket.

Multifunctional public service center
The newest public service center office building receives citizens and provides public services. Now all documents for individuals and legal entities can be issued in one place. Services include issuance of certificates for transportation of dangerous goods and registration of place of residence.

Automated warehouses
A single automated warehouse with shelving, a conveyor belt, and a loading area was built for online stores. Different areas automatically regulate the temperature depending on the type of goods; for example, medicines for online pharmacies are stored at a lower temperature. A dark store is available for local storage of goods.

Shopping and business center
City Housing and Utilities ensures the operation and maintenance of the shopping and business center premises, as well as monitors the condition of buildings, equipment, and entertainment areas

Banks
Key organizations: Central Bank of Standoff, Commercial Bank of Standoff, First Partner Bank, Global Digital Bank
Key organizations: Central Bank of Standoff, Commercial Bank of Standoff, First Partner Bank, Global Digital Bank
State S’s banking industry consists of one central and three commercial banks: Commercial Bank of Standoff, First Partner Bank, and Global Digital Bank.

Central Bank of Standoff
The money and credit regulator, responsible for currency issuance and the stable functioning of other banks in State S.

Commercial Bank of Standoff
The largest bank, serving 70 percent of the country’s adult population. The bank has two branches: central and western. They use different versions of core banking systems; the central branch utilizes a newer version.

First Partner Bank
A modern digital bank that primarily serves merchant accounts, which allow retail companies to accept payments using bank cards.
Remote service is provided through the eKassir platform. For convenience, members of the public can pay for goods by QR code and transfer money through a fast payments system.

Global Digital Bank
A newly established bank serving individuals and legal entities worldwide. Highly automated with two branches. All Global Digital Bank applications operate in the cloud.
The commercial banks interact and make mutual settlements with the Central Bank of Standoff using the ARM KBR system, which allows payments through correspondent accounts opened with the Central Bank.
All the commercial banks have developed online banking services, enabling customers to transfer money, make deposits, pay bills, and perform a wide range of other transactions without visiting a branch. Business-to-business payments are facilitated through cashless transactions.
All the commercial banks have developed online banking services, enabling customers to transfer money, make deposits, pay bills, and perform a wide range of other transactions without visiting a branch. Business-to-business payments are facilitated through cashless transactions.
Information security
Information technology is rapidly advancing in both nations: each has its own infrastructure, modern industrial control systems, and digital technology strategy.
As production capabilities have grown, so too have the risks, prompting the governments of both countries to implement security measures.
As production capabilities have grown, so too have the risks, prompting the governments of both countries to implement security measures.






